Spanish inflation fell again sharply in November
Spain's inflation figure fell again sharply in November and is now already four percentage points below its peak level in July. The decline will continue in the coming months
Spanish inflation falls for the fourth month in a row
Spanish inflation was 6.8% year-on-year in November, down from 7.3% in October. Over the month, consumer prices fell by 0.1%. The harmonised index was 6.6%, down from 7.3% in October. This development was mainly due to a fall in fuel prices last month, while they rose in November last year. Also, price increases for clothing and footwear were more moderate last month than in November 2021.
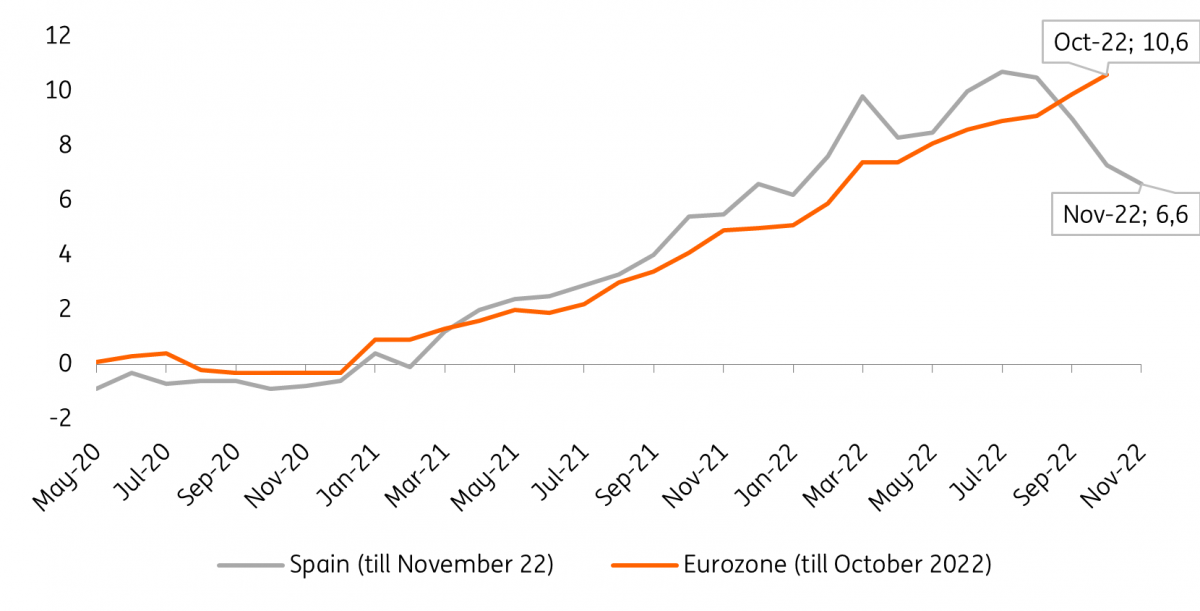
Spanish inflation now significantly below eurozone average
Spanish inflation has generally been above the eurozone average since the beginning of the year, but has fallen sharply since peaking at 10.7% in July. The weight of food in Spain is much higher than the eurozone average, which turbocharged the sharp price increases within this component. Hospitality also contributed more to price increases than the eurozone average, through a combination of faster rising prices but also a greater weight in the inflation basket.
After its peak level, Spanish inflation has fallen sharply, making it unique in the euro area. Energy inflation has fallen sharply and is well below the eurozone average. Energy prices in Spain rose sharply in autumn 2021, making the year-on-year comparison much weaker this year. Also the VAT cut on gas and electricity eased energy inflation. Details by component for November are not yet available, but October data showed that electricity inflation already turned negative last month (-15.4%) while also gas inflation fell sharply to 13.3% in October from 24.3% a month earlier. This decline will manifest itself further in the coming months.
Spain’s inflation slowdown has set in earlier
The light at the end of the inflation tunnel is getting brighter
Price pressures higher up the production chain are starting to ease. Both commodity prices, freight costs for transport and factory prices are starting to fall sharply from their recent peak levels. Last Friday, Spain's statistics office INE announced that producer prices fell again in October. While producer price inflation was still 42.9% in August, it fell to 26.1% in October, its lowest level since September 2021. Moreover, it is also becoming increasingly difficult for companies to implement new price increases as demand has fallen and inventories have risen sharply.
Inflation will gradually continue to normalise in 2023, but it will probably take until 2024 before inflation hovers around 2% again, the ECB's target. The development next year will depend on several factors, such as the prices of energy and other inputs on international markets, the fall in demand, the euro-dollar exchange rate and the speed at which falling prices higher up the production chain lead to lower prices for consumers. We expect inflation to reach 4.4% on average next year.
Author
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
